Scala for the Impatient 25 Mar 2014
第7章
3.
import scala.math._
package object random {
val a = 1664525
val b = 10131904223l
val mod = (BigInt(2) pow 32).toLong
var seed = 0
def setSeed(seed: Int) = this.seed = seed
def nextInt() = {
val result = ((seed * a + b) % mod).toInt
seed = result
result
}
def nextDouble() = 1.0 / nextInt()
}4.
可能是由于JVM的限制,包下面只能包含类,对象以及特质,而不能包含函数和变量
5.
private[com]将该方法的可见度限制在com包以及其子包,当然也需要注意练习2中的情况,以com来命名嵌套包,在实际使用中,尽量避免使用com,scala,org,java等命名嵌套包
6.
import java.util.{HashMap => JavaHashMap}
val javaMap = new JavaHashMap[String, Int]()
javaMap.put("Michael", 1)
import scala.collection.mutable.{HashMap => ScalaHashMap}
val map = new ScalaHashMap[String, Int]()
import collection.JavaConversions.mapAsScalaMap
for ((k, v) <- javaMap) map(k) = v
map同上
8.
将java和javax下面的所有类,对象,特质引入到当前上下文,如果该代码出现在org.easycloud,它将引入org.easycloud.java和org.easycloud.javax下面的类而不是顶部的java包和javax包,如果这两个包存在的话
PS. 由于java和javax包下没有任何类以及对象,所以两条引入语句其实没有用
9.
import java.lang.System._
val user = getProperty("user.name")
val password = readLine
if (password == "secret") println("Welcome, " + user) else err println "Sorry, your password is not correct"10.
StringBuilder, Byte, Boolean, Double, Float, Long,
第8章
1.
class BankAccount(initialBalance: Double) {
private var balance = initialBalance
def deposit(amount: Double) = {balance += amount; balance}
def withdraw(amount: Double) = { balance -= amount; balance}
}
class CheckingAccount(initialBalance: Double) extends BankAccount(initialBalance) {
private val charge = 1.0
override def deposit(amount: Double) = super.deposit(amount - charge)
override def withdraw(amount: Double) = super.withdraw(amount + charge)
}2.
class SavingsAccount(initialBalance: Double) extends BankAccount(initialBalance) {
private val monthlyInterestRate = 0.01
private[this] var freeChargeCount = 3
override def deposit(amount: Double) = {freeChargeCount -= 1; if (freeChargeCount >= 0) super.deposit(amount) else super.deposit(amount - 1.0)}
override def withdraw(amount: Double) = {freeChargeCount -= 1; if (freeChargeCount >= 0) super.withdraw(amount) else super.withdraw(amount + 1.0)}
def earnMonthlyInterest() = {super.deposit(monthlyInterestRate * super.deposit(0)); freeChargeCount = 3}
}3.
// Employee
// Manager
// WorkerBee
// SalesPerson
// Engineer
class Employee(val name: String, val dept: String = "general")
class Manager(name:String, dept:String = "general", val reports: Array[Employee]) extends Employee(name, dept)
class WorkerBee(name: String, dept:String = "general", val projects: Array[String]) extends Employee(name, dept)
class SalesPerson(name: String, override val dept: String = "sales", projects: Array[String], val quota: Int = 100) extends WorkerBee(name, dept, projects)
class Engineer(name: String, override val dept: String = "engineering", projects: Array[String], var machine: String = "") extends WorkerBee(name, dept, projects)4.
abstract class Item {
def price(): Double
def description(): String
}
class SimpleItem(val price: Double, val description: String) extends Item
class Bundle(val items: ArrayBuffer[Item]) extends Item {
def price(): Double = items.map(_.price).sum
def description: String = "Bundle:[" ++ (items.map(_.description) mkString ", ") ++ "]"
def addItem(item: Item) = items += item
}
val bundle = new Bundle(new ArrayBuffer[Item]())
bundle.addItem(new SimpleItem(3.0, "Iphone"))
bundle.addItem(new SimpleItem(4.0, "Ipad"))
bundle.addItem(new SimpleItem(5.0, "mac"))
bundle.price
bundle.description
val bigBundle = new Bundle(new ArrayBuffer[Item]())
bigBundle.addItem(new SimpleItem(1.0, "Apple Care"))
bigBundle.addItem(bundle)
bigBundle.price
bigBundle.description5.
class Point(val x: Double, val y: Double)
class LabeledPoint(val label: String, x: Double, y: Double) extends Point(x, y)6.
abstract class Shape {
def centerPoint(): Point
}
class Rectangle(val topLeftCorner: Point, val width: Double, val height: Double) extends Shape {
def centerPoint(): Point = new Point(topLeftCorner.x + width / 2.0, topLeftCorner.y - height / 2.0)
}
// override centerPoint with val
class Circle(val centerPoint: Point, val radius: Double) extends Shape7.
import java.awt.Rectangle
class Square(x: Int, y: Int, width: Int) extends Rectangle(x, y, width, width) {
def this(width: Int = 0) {
this(0, 0, width)
}
}8.
public class Person {
private final java.lang.String name;
public java.lang.String name();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #13 // Field name:Ljava/lang/String;
4: areturn
public java.lang.String toString();
Code:
0: new #18 // class scala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder
3: dup
4: invokespecial #22 // Method scala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder."<init>":()V
7: aload_0
8: invokevirtual #26 // Method java/lang/Object.getClass:()Ljava/lang/Class;
11: invokevirtual #31 // Method java/lang/Class.getName:()Ljava/lang/String;
14: invokevirtual #35 // Method scala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Lscala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder;
17: ldc #37 // String [name=
19: invokevirtual #35 // Method scala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Lscala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder;
22: aload_0
23: invokevirtual #39 // Method name:()Ljava/lang/String;
26: invokevirtual #35 // Method scala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Lscala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder;
29: ldc #41 // String ]
31: invokevirtual #35 // Method scala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Lscala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder;
34: invokevirtual #43 // Method scala/collection/mutable/StringBuilder.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
37: areturn
public Person(java.lang.String);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: aload_1
2: putfield #13 // Field name:Ljava/lang/String;
5: aload_0
6: invokespecial #45 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
9: return
}
public class SecretAgent extends Person {
private final java.lang.String name;
private final java.lang.String toString;
public java.lang.String name();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #14 // Field name:Ljava/lang/String;
4: areturn
public java.lang.String toString();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #18 // Field toString:Ljava/lang/String;
4: areturn
public SecretAgent(java.lang.String);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: aload_1
2: invokespecial #22 // Method Person."<init>":(Ljava/lang/String;)V
5: aload_0
6: ldc #24 // String secret
8: putfield #14 // Field name:Ljava/lang/String;
11: aload_0
12: ldc #24 // String secret
14: putfield #18 // Field toString:Ljava/lang/String;
17: return
}9.
将Creature中的range改为def,并将Ant子类的range也改为def,这样的话,env将被初始化为拥有两个0元素的数组,Ant构造器首先要构造Creature的构造器,由于range为方法,所以此时并不执行,它将先初始化env,而初始化env,需要调用range方法,该方法已经被Ant重写,方法最后结果反悔2,所以env被初始化为大小为2的数组; 将子类的range改为val后,env将被初始化为大小为0的数组,过程如下:Ant构造器首先要构造Creature的构造器,由于range为方法,所以此时并不执行,而初始化env,需要调用range,而range已经被子类覆写为range取值器,此时range还没有初始化,所以range返回0
10.
第一个protected含义是将Stack类的主构造器变为受保护的,这样只有Stack类及其子类可以访问它的主构造器,第二个protected用来将Stack的elems字段声明为protected,这样成员可以被Stack及其所有子类访问。
第9章
1.
import io.Source
val source = Source.fromFile("Person.scala")
val lines = source.getLines.toArray
source.close
import java.io.PrintWriter
val out = new PrintWriter("Person.reverse.txt")
for (line <- lines.reverse) out.println(line)
out.close2.
import io.Source
import java.io.PrintWriter
val source = Source fromFile "tabbed.txt"
val lines = source.getLines.toArray
source.close
val minSplits = 3
val maxLength = (for (line <- lines; token <- line.split("""\t""")) yield token.length).max
val length = maxLength + minSplits
val out = new PrintWriter("tabbed.txt")
for (line <- lines) { // 有没有可能将输出和计算最大长度合并在一个循环里呢
for (token <- line.split("""\t""")) out.print(token + " " * (length - token.length))
out.println
}
out.close3.
for (token <- Source.fromFile("words.txt").mkString.split("""\s+""") if token.length > 12) println(token) // Cheers!4.
import io.Source
val source = Source.fromFile("nums.txt")
val numbers = source.mkString.split("""\s+""").map(_.toDouble)
source.close
val sum = numbers.sum
println(sum)
println(sum / numbers.size)
println(numbers.max)
println(numbers.min)5.
import scala.math.BigInt
for (i <- 0 to 20) { val pow = BigInt(2) pow i; out.println(" " * (15 - pow.toString.length) + pow + " " * 8 + 1.0 / pow.toInt) }
out.close6.
import scala.util.matching.Regex
import io.Source
val stringPattern = """"(?:\"|.*)"""".r // the regex is "(?:\"|.*)"
val source = Source.fromFile("WeiXinSearcherController.java")
val javaSources = source.mkString
for (matchString <- stringPattern findAllIn javaSources) println(matchString)
source.close7.
val source = Source.fromFile("nums.txt")
for (split <- source.mkString.split("""-?\d+.\d+""")) println(split)
source.close8.
val imgSrcPattern = """<img[^>]+src\s*=\s*['\"]([^'\"]+)['\"][^>]*>""".r
val source = Source.fromFile("index.html")
for (imgSrcPattern(imgSrc) <- imgSrcPattern findAllIn source.mkString) println(imgSrc)9.
import java.nio.file._
implicit def makeFileVisitor(f: (Path) => Unit) = new SimpleFileVisitor[Path] {
override def visitFile(p: Path, attrs: attribute.BasicFileAttributes) = {
f(p)
FileVisitResult.CONTINUE
}
}
var i = 0
val dir = new java.io.File("/Users/ibntab")
Files.walkFileTree(dir.toPath, (f: Path) => { val file = f.toFile; if (file.isFile && file.getName.endsWith(".class")) i += 1})
println(i)10.
@SerialVersionUID(43L) class Person(val name: String, val friends: ArrayBuffer[Person] = new ArrayBuffer[Person]) extends Serializable {override def toString: String = name}
val fred = new Person("fred")
val michael = new Person("michael")
val etta = new Person("etta")
val carl = new Person("carl")
val alex = new Person("alex")
michael.friends append etta
michael.friends append carl
carl.friends append alex
carl.friends append fred
val wearefriends = Array(fred, michael, etta, carl, alex)
import java.io._
val out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("friends"))
out.writeObject(wearefriends)
out.close
val in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("friends"))
val friends = in.readObject.asInstanceOf[Array[Person]]
friends(1).friends
friends(3).friends
// output scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[Person] = ArrayBuffer(etta, carl)
// output scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[Person] = ArrayBuffer(alex, fred)第10章
1.
trait RectangleLike {
def translate(dx: Int, dy: Int) = { setFrame(getX + dx, getY - dy, getWidth, getHeight) }
def grow(h: Int, v: Int) = { setFrame(getX - h, getY + v, getWidth + 2 * h, getHeight + 2 * v) }
def getX(): Double
def getY(): Double
def getWidth(): Double
def getHeight(): Double
def setFrame(x: Double, y: Double, width: Double, height: Double)
}2.
import java.awt.Point
class OrderedPoint(x: Int, y: Int) extends Point(x: Int, y: Int) with math.Ordered[Point] {
def compare(that: Point): Int = {
if (this.getX > that.getX) 1
else if (this.getX < that.getX) -1
else {
if (this.getY > that.getY) 1
else if (this.getY < that.getY) -1
else 0
}
}
}
val p1 = new OrderedPoint(-1, 1)
val p2 = new OrderedPoint(1, 1)
val p3 = new OrderedPoint(1, 2)
val p4 = new OrderedPoint(1, 2)
p1 < p2; p2 < p3; p3 == p43.
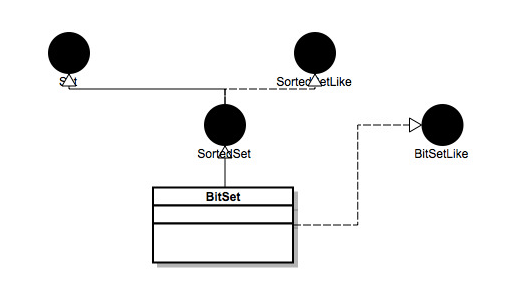
lin(BitSet) = BitSet >> lin(BitSetLike) >> lin(SortedSet) = BitSet >> (BitSetLike >> lin(SortedSetLike)) >> (SortedSet >> lin(SortedSetLike) >> lin(Set)) = BitSet >> BitSetLike >> SortedSet >> SortedSetLike >> Set
4.
trait Logger {
def log(msg: String) = {}
}
trait ConsoleLogger extends Logger {
override def log(msg: String) = println(msg)
}
trait CryptoLogger extends Logger {
val offset: Int = 3
override def log(msg: String) = super.log(msg.map(_ + offset).map(_.toChar).mkString)
}
class TestLogger extends Logger {
def doSomeWork() = log("do some stupid work")
}
val test1 = new TestLogger with ConsoleLogger
test1.doSomeWork
val test2 = new TestLogger with ConsoleLogger with CryptoLogger
test2.doSomeWork
val test3 = new TestLogger with ConsoleLogger with CryptoLogger {
override val offset: Int = -3
}
test3.doSomeWork
val test4 = new {override val offset: Int = -3} with TestLogger with ConsoleLogger with CryptoLogger
test4.doSomeWork5.
trait PropertyChangeSupportLike {
val pcs = new PropertyChangeSupport(this)
def addPropertyChangeListener(listener: PropertyChangeListener) = pcs.addPropertyChangeListener(listener)
def addPropertyChangeListener(propertyName: String, listener: PropertyChangeListener) = pcs.addPropertyChangeListener(propertyName, listener)
def fireIndexedPropertyChange(propertyName: String, index: Int, oldValue: Boolean, newValue: Boolean) = pcs.fireIndexedPropertyChange(propertyName, index, oldValue, newValue)
def fireIndexedPropertyChange(propertyName: String, index: Int, oldValue: Int, newValue: Int) = pcs.fireIndexedPropertyChange(propertyName, index, oldValue, newValue)
def fireIndexedPropertyChange(propertyName: String, index: Int, oldValue: Object, newValue: Object) = pcs.fireIndexedPropertyChange(propertyName, index, oldValue, newValue)
def firePropertyChange(event: PropertyChangeEvent) = pcs.firePropertyChange(event)
def firePropertyChange(propertyname: String, oldValue: Boolean, newValue: Boolean) = pcs.firePropertyChange(propertyname, oldValue, newValue)
def firePropertyChange(propertyName: String, oldValue: Int, newValue: Int) = pcs.firePropertyChange(propertyName, oldValue, newValue)
def firePropertyChange(propertyName: String, oldValue: Object, newValue: Object) = pcs.firePropertyChange(propertyName, oldValue, newValue)
def getPropertyChangeListeners(): Array[PropertyChangeListener] = pcs.getPropertyChangeListeners
def getPropertyChangeListeners(propertyName: String): Array[PropertyChangeListener] = pcs.getPropertyChangeListeners(propertyName)
def hasListeners(propertyName: String): Boolean = pcs.hasListeners(propertyName)
def removePropertyChangeListener(listener: PropertyChangeListener) = pcs.removePropertyChangeListener(listener)
def removePropertyChangeListener(propertyName: String, listener: PropertyChangeListener) = pcs.removePropertyChangeListener(propertyName, listener)
}
val beanSupportPoint = new java.awt.Point(0, 0) with PropertyChangeSupportLike6.
Java中只能单继承,JContainer不能同时继承自JComponent和Container
trait JComponent extends Component
class JContainer extends Container with JComponent7.
trait Top {
def add() = {}
}
trait Tomato extends Top {
override def add() = { print(" tomato "); super.add }
}
trait Beaf extends Top {
override def add() = { print(" beaf "); super.add }
}
class Pizza extends Top {
def introduceMyself() { print(" a pizza"); add; println() }
}
val aPizza = new Pizza with Beaf with Tomato
aPizza.introduceMyself8.
import java.io._
trait BufferLike {
this: InputStream =>
val BUFFER_SIZE = 20
val buffer = new Array[Byte](BUFFER_SIZE)
var pos = 0
var count = 0
override def read(): Int = {
if (pos >= count) {
count = this.read(buffer, 0, BUFFER_SIZE)
pos = 0
}
if (pos >= count) {
-1
} else {
pos += 1
buffer(pos - 1)
}
}
}
val fis = new FileInputStream("logs/erm.log") with BufferLike
fis.read9.
import java.io._
trait Logger {
def log(msg: String) {}
}
trait ConsoleLogger extends Logger {
override def log(msg: String) = println(msg)
}
trait BufferLike extends Logger {
this: InputStream =>
val BUFFER_SIZE = 5
val buffer = new Array[Byte](BUFFER_SIZE)
var pos = 0
var count = 0
override def read(): Int = {
if (pos >= count) {
count = this.read(buffer, 0, BUFFER_SIZE)
if (count > 0) {
log("Read into the buffer, size: [" + count + "]")
} else {
log("the end of buffer")
}
pos = 0
}
if (pos >= count) {
-1
} else {
pos += 1
buffer(pos - 1)
}
}
}
val fis = new FileInputStream("logs/erm.log") with BufferLike with ConsoleLogger
fis.read10.
import java.io._
trait IterableInputStream extends InputStream with Iterable[Byte] { is =>
class InputStreamIterator extends Iterator[Byte] {
def hasNext() = is.available > 0
def next() = is.read.toByte
}
def iterator = new InputStreamIterator
}
val f = new java.io.FileInputStream("test9.txt") with IterableInputStream第11章
1.
3 + 4 -> 5 先执行3+4得7,然后再执行7 -> 5,得到(7, 5)的对偶 3 -> 4 + 5 先执行 3 -> 4 得到(3, 4)对偶,再执行+5,但类型不符,所以语句执行失败 因为+ - 操作符的优先级是一样的
2.
由于乘方一般优先于乘法执行,而 ** 与 * 的执行优先级相同,所以没有采用**,而采用 ^,优先级要低于 * ,所以也不采用 ^
3.
class Fraction (n: Int, d: Int) {
private val num: Int = if (d == 0) 1 else n * sign(d) / gcd(n, d)
private val den: Int = if (d == 0) 0 else d * sign(d) / gcd(n, d)
override def toString = num + "/" + den
def sign(a: Int) = if (a > 0) 1 else if (a < 0) -1 else 0
def gcd(a: Int, b: Int): Int = if (b == 0) abs(a) else gcd(b, a % b)
def + (f: Fraction) = new Fraction(num * f.den + den * f.num, den * f.den)
def - (f: Fraction) = new Fraction(num * f.den - den * f.num, den * f.den)
def * (f: Fraction) = new Fraction(num * f.num, den * f.den)
def / (f: Fraction) = new Fraction(num * f.den, den * f.num)
def abs(a: Int) = if (a > 0) a else if (a < 0) -a else 0
}4.
import scala.math.Ordered
class Money(d: Int, c: Int) extends Ordered[Money] {
private val dollars: Int = d + c / 100
private val cents: Int = c % 100
override def toString = "$%d.%d".format(dollars, cents) // Need to be perfected
def toCents() = dollars * 100 + cents
def fromCents(c: Int) = new Money(c / 100, c % 100)
def + (m: Money) = fromCents(toCents + m.toCents)
def - (m: Money) = fromCents(toCents - m.toCents)
def compare(that: Money) = toCents - that.toCents
}5.
import collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
class Table {
val buffer = new ArrayBuffer[String]()
def | (colValue: String) = { buffer += "<td>%s</td>" format colValue; this }
def || (colValue: String) = { buffer += "</tr><tr><td>%s</td>" format colValue; this }
override def toString = "<table><tr>%s</tr></table>" format buffer.mkString("")
}
object Table {
def apply() = new Table
}
Table() | "Java" | "Scala" || "Gosling" | "Odersky" || "JVM" | "JVM, .NET"6.
class ASCIIArt(val str: String) {
def + (that: ASCIIArt) = str.split("\n").zip(that.str.split("\n")).map(line => line._1 + line._2).mkString("\n")
def ^ (that: ASCIIArt) = str + "\n" + that.str
}
val a = new ASCIIArt(
"""
/\_/\
( ' ' )
( - )
| | |
(__|__)
"""
)
val b = new ASCIIArt(
"""
-----
/ Hello \
< Scala |
\ Coder /
-----
"""
)7.
class BitSequence(var bits: Long = 0) {
def apply(index: Int) = if ((bits & (1l << index % 64)) > 0) 1 else 0
def update(index: Int, bit: Int) = if ((bit & 1l) > 0) bits |= (1l << (index % 64)) else bits &= ~(1l << index % 64)
override def toString = "%64s".format(bits.toBinaryString).replaceAll(" ", "0")
}
val x = new BitSequence
x(45) = 1
x(45)8.
class Matrix(val m: Int = 2, val n: Int = 2) {
private val matrix = Array.ofDim[Double](m, n)
def apply(col: Int, row: Int) = matrix(col)(row)
def update(col: Int, row: Int, value: Double) = matrix(col)(row) = value
def + (that: Matrix) = {
require(m == that.m)
require(n == that.n)
val result = new Matrix(m, n)
for (i <- 0 until m; j <- 0 until m) result(i, j) = this(i, j) + that(i, j)
result
}
def - (that: Matrix) = this + that * -1
def * (factor: Double) = {
val result = new Matrix(m, n)
for (i <- 0 until m; j <- 0 until n) result(i, j) = this(i, j) * factor
result
}
def * (that: Matrix) = {
require(n == that.m)
val result = new Matrix(m, that.n)
for (i <- 0 until m; j <- 0 until that.n) result(i, j) = prod(i, j, that)
result
}
private def prod(i: Int, j: Int, that: Matrix) = (for (k <- 0 until n) yield this(i, k) * that(k, j)).sum
override def toString = matrix.map(_.mkString(" ")).mkString("\n")
}
val a = new Matrix(3, 4)
val b = new Matrix(3, 4)
a(0, 0) = 1.0
b(2, 1) = 3.4
a + b
val c = new Matrix(3, 2)
val d = new Matrix(2, 4)
c(1, 1) = 3.0
c(1, 0) = 8.0
d(0, 1) = 4.0
d(1, 3) = 5.0
val e = c * d
e * 39.
object RichFile {
def unapply(path: String) = {
val suffixIdx = path lastIndexOf "."
val (fullPath, suffix) = (path.substring(0, suffixIdx), path.substring(suffixIdx + 1))
val split = path lastIndexOf "/"
Some((fullPath.substring(0, split), fullPath.substring(split + 1), suffix))
}
}
val RichFile(dir, fileName, suffix) = "/home/cay/readme.txt"10.
object RichFile {
def unapplySeq(path: String): Option[Seq[String]] = {
if (path == "") None else Some(path.trim.split("/"))
}
}
val RichFile(first, middle, last) = "home/user/text.txt"
println("First: %s, Middle: %s, Last: %s".format(first, middle, last))第12章
1.
def values(fun: (Int) => Int, low: Int, high: Int) = for (i <- low to high) yield i -> fun(i)
values(x => x * x, -5, 5)
// or another way
def values(fun: (Int) => Int, low: Int, high: Int) = (low to high) map (i => i -> fun(i))2.
import scala.math._
val arr = Array[Int](8, 0, 23, -23, 32, 75, 2, -99, 20, 74, 75, 20, 43)
arr.reduceLeft(max(_, _))3.
def factorial(n: Int) = (1 to n).reduceLeft(_ * _)4.
def factorial(n: Int) = (1 to n).foldLeft(1)(_ * _)5.
def largest(fun: (Int) => Int, inputs: Seq[Int]): Int = inputs.map(fun(_)).max
largest(x => 10 * x - x * x, 1 to 10)6.
def largestAt(fun: (Int) => Int, inputs: Seq[Int]) = inputs.map(x => x -> fun(x)).reduceLeft((x, y) => (if (x._2 > y._2) x else y))._1
largestAt(x => 10 * x - x * x, 1 to 10)7.
def adjustToPair(fun: (Int, Int) => Int) = (pair: (Int, Int)) => fun(pair._1, pair._2)
adjustToPair(_ * _)((6, 7))8.
val a = Array[String]("Hello world", "Hi, Meng", "hahah", "blah-blah")
val b = Array[Int](11, 8, 5, 9)
a.corresponds(b)(_.length == _)9.
def corresponds(a: Seq[String], b: Seq[Int], fun: (String, Int) => Boolean) = a.zip(b).map(x => fun(x._1, x._2)).count(!_) == 0
val a = Array[String]("Hello world", "Hi, Meng", "hahah", "blah-blah")
val b = Array[Int](11, 8, 5, 9)
corresponds(a, b, (x, y) => x.length == y)10.
def unless(condition: => Boolean)(block: => Unit) = if (!condition) block
val i = 1
unless(i == 1) {println("It's one")}
val b = 2
unless(b == 1) {println("It's one")}第13章
1.
由于使用了LinkedhashSet,可以保证集内元素顺序与插入顺序一致,而可以保证下标是按顺序插入得
import collection.mutable.{LinkedHashSet, Map}
def indexes(str: String) = {
(Map[Char, LinkedHashSet[Int]]() /: (str.zipWithIndex)) {
(m, p) => m + (p._1 -> (m.getOrElse(p._1, LinkedHashSet[Int]()) += p._2))
}
}2.
import collection.immutable.{List, Map}
def indexes(str: String) = {
(Map[Char, List[Int]]() /: (str.zipWithIndex)) {
(m, p) => m + (p._1 -> (m.getOrElse(p._1, List[Int]()) :+ p._2))
}
}3.
import collection.mutable.{LinkedList}
def removeZero(lst: LinkedList[Int]) = lst.filter(_ != 0)
val list = LinkedList[Int](0, 1, -1, 0, 3, 4, 0, 4, 3, 0, 9, 0)
removeZero(list)4.
import collection.immutable.Map
def indexes(words: Array[String], dicts: Map[String, int]) = words flatMap dicts.get(_)
val arr = Array("Tom", "Fred", "Harry")
val dicts = Map("Tom" -> 3, "Dick" -> 4, "Harry" -> 5)
indexes(arr, dicts)5.
def mkString(arr: Array[String], split: String) = arr.reduceLeft(_ + split + _)
mkString(Array("Tom", "Fred", "Harry", "Dick"), "/")6.
给定整型列表lst, (lst :\ List[Int]())(_ :: _)得到的结果列表与lst顺序一致,(List[Int]() /: lst)(_ :+ _)得到的结果列表与lst顺序一致
如果需要对列表反向排列,第一条语句修改为
(List(1, 2, 4, 5, 6) :\ List[Int]()) {
(elem, lst) => lst :+ elem
}第二条语句修改为
(List[Int]() /: List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) {
(lst, elem) => elem +: lst
}7.
(Array(2.03, 4.2, 7.8) zip Array(3, 5, 2)) map {Function tupled (_ * _)}8.
def group(arr: Array[Double], cols: Int) = (arr grouped cols).toArray9.
并行的修改SynchronizedMap并不安全,而第二种方式是可以安全的修改Map中的值的
10.
由于frequencies并不是线程安全的,多个线程同时修改它会有数据不一致(线程安全)问题
str.par.aggregate(Map[Char, Int]()) (
(r, c) => r + (c -> (r.getOrElse(c, 0) + 1)),
(m1, m2) => m1 ++ m2 map {case (k, v) => k -> (v + m1.getOrElse(k, 0) + 1)}
)第14章
2.
def swap(pair: Tuple2[Int, Int]) = pair match {
case (x, y) => (y, x)
}
swap(1 -> 2)3.
def swap(arr: Array[Int]) = arr match {
case Array(x, y, rest @ _*) => Array(y, x) ++ rest
case _ => arr
}
swap(Array(1, 2, 3 ,4 ,5))
swap(Array(1))4.
abstract class Item
case class Article(description: String, price: Double) extends Item
case class Bundle(description: String, discount: Double, items: Item*) extends Item
case class Multiple(count: Int, item: Item) extends Item
def price(item: Item): Double = item match {
case Article(_, p) => p
case Bundle(_, disc, its @ _*) => its.map(price _).sum - disc
case Multiple(c, it) => c * price(it)
}
val m = Multiple(10, Bundle("Father's day special", 20.0, Article("Scala for the Impatient", 39.95),
Bundle("Anchor Distillery Sampler", 10.0,
Article("Old Potrero Straight Rye Whisky", 79.95),
Article("Junipero Gin", 32.95))))
println(price(m))
val m2 = Multiple(10, Article("Blackwell Toster", 29.95))
println(price(m2))5.
import collection.immutable.List
def leafSum(list: List[Any]): Int = {
list.map(_ match {
case l: List[Any] => leafSum(l)
case i: Int => i
case _ => 0
}).sum
}6.
sealed abstract class BinaryTree
case class Leaf(value: Int) extends BinaryTree
case class Node(left: BinaryTree, right: BinaryTree) extends BinaryTree
def sum(tree: BinaryTree): Int = tree match {
case Leaf(v) => v
case Node(l, r) => sum(l) + sum(r)
}
sum(Node(Node(Leaf(8), Node(Leaf(1), Leaf(2))), Leaf(3)))7.
sealed abstract class Tree
case class Leaf(value: Int) extends Tree
case class Node(children: Tree*) extends Tree
def sum(tree: Tree): Int = tree match {
case Leaf(v) => v
case Node(ch @ _*) => ch.map(sum _).sum
}
sum(Node(Node(Leaf(3), Leaf(8)), Leaf(2), Node(Leaf(5))))8.
sealed abstract class Tree
case class Leaf(value: Int) extends Tree
case class Node(op: Char, children: Tree*) extends Tree
def eval(tree: Tree): Int = tree match {
case Leaf(v) => v
case Node(op, ch @ _*) => op match {
case '+' => ch.map(eval _).sum
case '-' => -ch.map(eval _).sum
case '*' => ch.map(eval _).product
}
}
eval(Node('+', Node('*', Leaf(3), Leaf(8)), Leaf(2), Node('-', Leaf(5))))9.
import collection.immutable.List
def sum(list: List[Option[Int]]) = list.map(_ getOrElse 0).sum10.
(这道题有问题吧。。。)
import math.sqrt
def compose(f: (Double) => Option[Double], g: (Double) => Option[Double]): (Double) => Option[Double] = (x: Double) => f(x) match {
case Some(d) => g(d) match {
case Some(dd) => Some(dd)
case None => None
}
case None => None
}
def f(x: Double) = if (x >= 0) Some(sqrt(x)) else None
def g(x: Double) = if (x != 1) Some(1 / (x - 1)) else None
val h = compose(f, g)
h(2)
h(1)
h(0)第17章
1.
class Pair[T, S](val t: T, val s: S) {
def swap() = new Pair[S, T](s, t)
override def toString() = "(" + t + ", " + s + ")"
}
new Pair(5, "Hello").swap()2.
class Pair[T](var a: T, var b: T) {
def swap() = {val temp = a; a = b; b = temp}
override def toString() = "(%1, %2)".format(a, b)
}
new Pair(4, 6).swap3.
class Pair[T, S] {
def swap[T, S](pair: (T, S)) = pair._2 -> pair._1
}
new Pair().swap(1, "Hello")4. 由于Student为Person的子类,将一个Student实例传递给replaceFirst方法后返回Pair[Person]
第20章
1.
import scala.util.Random
import scala.actors.{Channel, OutputChannel, Actor}
import scala.actors.Actor._
/**
* Created by ibntab on 13-11-13.
*/
object ConcurrentAvg extends App {
val n = 1000000
val size = n / 20
val arr = for (i <- 1 to n) yield Random.nextDouble()
println("Init Done")
case class Sum(input: Seq[Double], result: OutputChannel[Double])
class SumActor extends Actor {
def act() = {
while (true) {
receive {
case Sum(input, out) => { val answer = input.sum; out ! answer }
}
}
}
}
actor {
val channel = new Channel[Double]
arr.grouped(size).foreach {
val sumActor = new SumActor
sumActor.start()
sumActor ! Sum(_, channel)
}
val start = System.currentTimeMillis()
var sum = 0.0
for (i <- 1 to 20) {
channel.receive {
case x => sum += x
}
}
println("result: " + sum / n)
println("Con time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start))
}
val start = System.currentTimeMillis()
println("s result: " + arr.sum / n)
println("S time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start))
}