ScalaTest and ScalaCheck 08 Jul 2014
ScalaCheck是基于属性声明和测试数据自动化生成的Scala和Java程序的测试工具。它的基本理念是对方法或代码单元的预期行为声明属性,然后会检查这些声明的属性能通过测试。ScalaCheck以随机方式自动生成所有的测试数据,因此测试者不必担心任何遗漏的测试用例。
使用ScalaTest,我们可以测试我们的Scala代码和Java代码;它提供了Junit,TestNG,ScalaCheck以及EasyMock等常见的测试工具,ScalaTest提供了多种代码风格可供我们选择
ScalaTest Styles
FunSuite
近似于Junit的样式, 并且能够生成Specification形式的测试输出
import org.scalatest.FunSuite
class SetSuite extends FunSuite {
test("An empty Set should have size 0") {
assert(Set.empty.size == 0)
}
test("Invoking head on an empty Set should produce NoSuchElementException") {
intercept[NoSuchElementException] {
Set.empty.head
}
}
}FlatSpec
从xUnit迁移到BDD最简单的形式,和xUnit仍然很相像。但是测试名必须行为”A should B”
import org.scalatest.FlatSpec
class SetSpec extends FlatSpec {
"An empty Set" should "have size 0" in {
assert(Set.empty.size == 0)
}
it should "produce NoSuchElementException when head is invoked" in {
intercept[NoSuchElementException] {
Set.empty.head
}
}
}FunSpec
对于Ruby的RSpecs的用户来说,可能更喜欢该种形式
import org.scalatest.FunSpec
class SetSpec extends FunSpec {
describe("A Set") {
describe("when empty") {
it("should have size 0") {
assert(Set.empty.size == 0)
}
it("should produce NoSuchElementException when head is invoked") {
intercept[NoSuchElementException] {
Set.empty.head
}
}
}
}
}WordSpec
对于Specs和Specs2的用户来说,可能更喜欢该种形式
import org.scalatest.WordSpec
class SetSpec extends WordSpec {
"A Set" when {
"empty" should {
"have size 0" in {
assert(Set.empty.size == 0)
}
"produce NoSuchElementException when head is invoked" in {
intercept[NoSuchElementException] {
Set.empty.head
}
}
}
}
}FreeSpec
import org.scalatest.FreeSpec
class SetSpec extends FreeSpec {
"A Set" - {
"when empty" - {
"should have size 0" in {
assert(Set.empty.size == 0)
}
"should produce NoSuchElementException when head is invoked" in {
intercept[NoSuchElementException] {
Set.empty.head
}
}
}
}
}Spec
import org.scalatest.Spec
class SetSpec extends Spec {
object `A Set` {
object `when empty` {
def `should have size 0` {
assert(Set.empty.size == 0)
}
def `should produce NoSuchElementException when head is invoked` {
intercept[NoSuchElementException] {
Set.empty.head
}
}
}
}
}PropSpec
import org.scalatest._
import prop._
import scala.collection.immutable._
class SetSpec extends PropSpec with TableDrivenPropertyChecks with Matchers {
val examples =
Table(
"set",
BitSet.empty,
HashSet.empty[Int],
TreeSet.empty[Int]
)
property("an empty Set should have size 0") {
forAll(examples) { set =>
set.size should be (0)
}
}
property("invoking head on an empty set should produce NoSuchElementException") {
forAll(examples) { set =>
a [NoSuchElementException] should be thrownBy { set.head }
}
}
}FeatureSpec
import org.scalatest._
class TVSet {
private var on: Boolean = false
def isOn: Boolean = on
def pressPowerButton() {
on = !on
}
}
class TVSetSpec extends FeatureSpec with GivenWhenThen {
info("As a TV set owner")
info("I want to be able to turn the TV on and off")
info("So I can watch TV when I want")
info("And save energy when I'm not watching TV")
feature("TV power button") {
scenario("User presses power button when TV is off") {
Given("a TV set that is switched off")
val tv = new TVSet
assert(!tv.isOn)
When("the power button is pressed")
tv.pressPowerButton()
Then("the TV should switch on")
assert(tv.isOn)
}
scenario("User presses power button when TV is on") {
Given("a TV set that is switched on")
val tv = new TVSet
tv.pressPowerButton()
assert(tv.isOn)
When("the power button is pressed")
tv.pressPowerButton()
Then("the TV should switch off")
assert(!tv.isOn)
}
}
}以下都选择使用WordSpec
完成第一个TEST
import org.scalatest.WordSpec
import scala.collection.mutable
/**
* Created by ibntab on 14/7/8.
*/
class HelloWorldSpec extends WordSpec {
"A Stack" must {
"get values in last-in-first-out order" when {
"popping" in {
val stack = new mutable.Stack[Int]
stack.push(1)
stack.push(2)
assert(stack.pop() === 2)
assert(stack.pop() === 1)
}
}
"throw NoSuchElementException" when {
"it is empty" in {
val emptyStack = new mutable.Stack[String]
intercept[NoSuchElementException] {
emptyStack.pop()
}
}
}
}
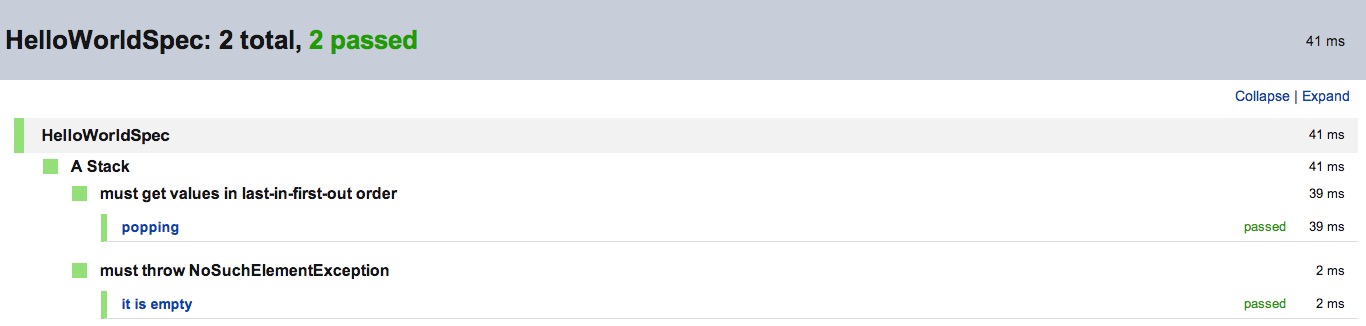
}运行后它将生成类似以下测试结果
使用Assertions
可以向assert中传入一个Boolean表达式,如果Boolean表达式返回的结果为true,则通过测试,否则Fail
assert(1 == 2)上面代码只会提示assert失败,如果希望有更易懂的提示信息,可以使用如下代码
assert(1 === 2)上述代码会提示”1 did not equal 2”
可以使用intercept来测试代码是否抛出预期的异常
val s = "hi"
val thrown = intercept[IndexOutOfBoundsException] {
s.charAt(-1)
}
assert(thrown.getMessage === "String index out of range: -1")使用BeforeAndAfter抽取公共逻辑
类似于Junit中的@Before和@After之流,scalatest中可以混入BeforeAndAfter特质
import org.scalatest.{BeforeAndAfter, WordSpec}
import scala.collection.mutable
/**
* Created by ibntab on 14/7/8.
*
*/
class HelloWorldSpec extends WordSpec with BeforeAndAfter {
var stack: mutable.Stack[Int] = _
before {
stack = new mutable.Stack[Int]
}
"A Stack" must {
"get values in last-in-first-out order" when {
"popping" in {
stack.push(1)
stack.push(2)
assert(stack.pop() === 2)
assert(stack.pop() === 1)
}
}
"throw NoSuchElementException" when {
"it is empty" in {
intercept[NoSuchElementException] {
stack.pop()
}
}
}
}
after {
...
}
}Assertions
ScalaCheck的几个概念
- 属性Properties 属性Properties是ScalaTest的一个基本测试单元,类似于Junit或TestNG中的一个测试方法(用
@Test注解)